The diagnostic test for glaucoma includes a series of tests
The diagnostic test for glaucoma includes a series of tests, which although are easy and painless, they however, require great cooperation from the patient.
The most important examination in the study of glaucoma is the tonometry, which is the measurement of intraocular pressure. Checking the drainage of the aqueous humor (the "angle") is done with a special lens, which comes into contact with the patient's eye. The examination is called gonioscopy.
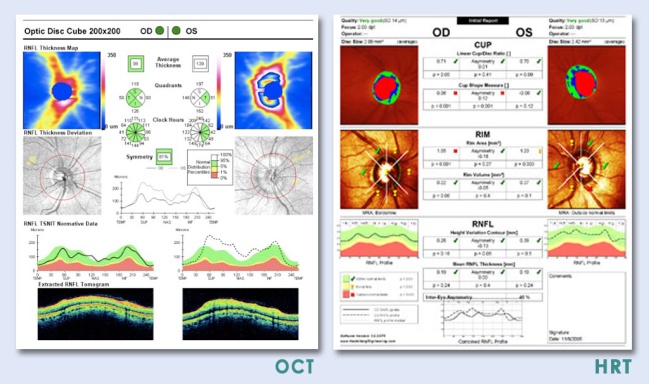
A pupilloscopy is necessary to control the integrity of the optic nerve, and now with the evolution of technology, a daily practice includes a detailed analysis of the optic nerve’s head by using special cameras and computer systems, such as the OCT, the HRT and GDx.
The extent of damage to the patient’s visual field, who predominantly is affected by glaucoma, is assessed by using machines called perimetry (or simply "fields").
All these tests require immobility and great cooperation from the patient. The attempt to do these tests to a small child is in most cases practically impossible. Even a simple measurement of blood pressure can be particularly problematic in a restless child.
A partial solution to the problem is granting general anesthesia. This allows the implementation of tests that require immobility, such as measuring the diameter of the cornea, the controlling of the angle and the pupiloscopy, but not those that depend solely on the cooperation of the child, such as the visual fields. Although tonometry under general anesthesia is feasible, it seems to give lower intraocular pressure values and is not always reliable.
However, as already mentioned, glaucoma in children is very rare and there is no need to check for it if there are no other symptoms, such as clouding of the cornea, intense photophobia and especially the growth or size asymmetry of the eye. Only then the ophthalmologist will take into account all the factors and decide if there should be a more detailed checking under general anesthesia.
 German
German Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά