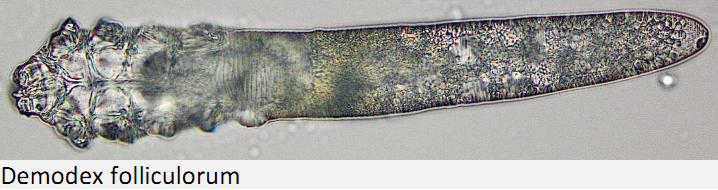
The role of "Demodex" mites with dry eyes Demodex mites are ectoparasites, living on the human being. They are very common and usually located around the nose and the eyelids. These, 150-350μm long, parasites live and stay at the exits of hair follicles/eyelashes, or even at the exit passage of the meibomian glands. They feed themselves with cytoplasm and also from the surrounding secretions.

Eyelash with demodex infestation
In the case of dry eyes, they can play a role in meibomian gland dysfunction and chronic blepharitis/inflammations. The doctor can see a hint for demodex infestation on the lid margin (at the slitlamp). The lid margin is more red than usual and yellowish crusts around single eyelashes can be seen. The doctor can ensure the individual case with the help of a microscope. B. oleronius (bacteria), which most probably functions as a co-pathogen in the development of blepharitis, is coexisting with demodex mites. B. oleronius produces enzymes, that are capable of splitting lipids, thus enhancing the dry eye syndrome even more.
 German
German Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά